Hydraulic Jump Stilling Basin Examples: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<!-- Add body paragraphs here --> | <!-- Add body paragraphs here --> | ||
[[Energy Dissipation|Energy dissipation]] in a Hydraulic Jump Stilling Basin is accomplished by forcing a hydraulic jump in the basin structure. | [[Energy Dissipation|Energy dissipation]] in a Hydraulic Jump Stilling Basin is accomplished by forcing a hydraulic jump in the basin structure. | ||
<gallery mode= | <gallery mode=packed-hover heights=300px> | ||
<!-- Add image files here --> | <!-- Add image files here --> | ||
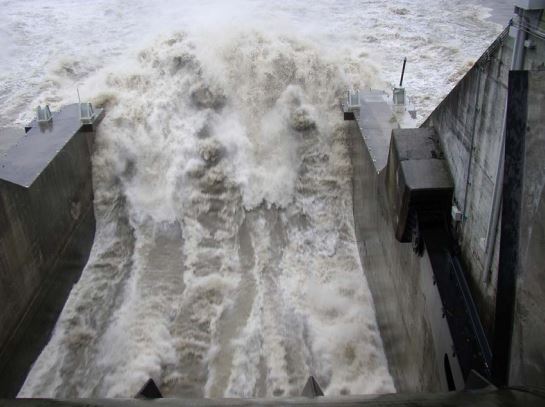
File:HJ1.jpg|Example of a Hydraulic Jump in a stilling basin. (Image courtesy www.engr.colostate.edu) | File:HJ1.jpg|Example of a Hydraulic Jump in a stilling basin. (Image courtesy www.engr.colostate.edu) | ||
Revision as of 22:17, 25 April 2023
Energy dissipation in a Hydraulic Jump Stilling Basin is accomplished by forcing a hydraulic jump in the basin structure.
-
Example of a Hydraulic Jump in a stilling basin. (Image courtesy www.engr.colostate.edu)
-
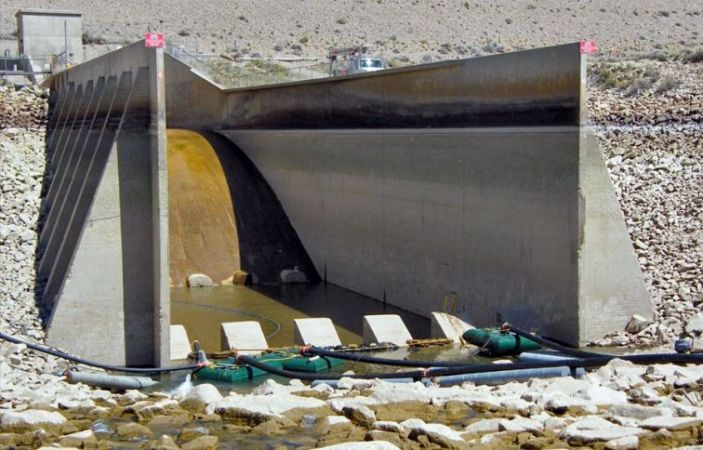
Type II stilling basin with counterforted walls. The basin has been unwatered for repairs.
-
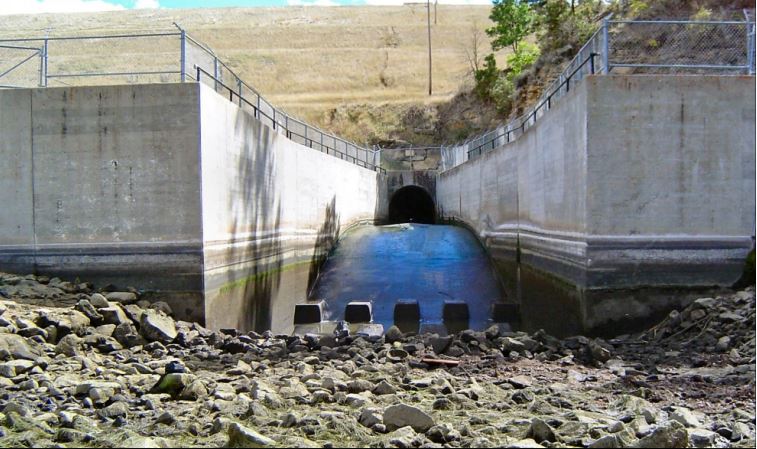
Wingwalls oriented normal to the basin side walls.
-
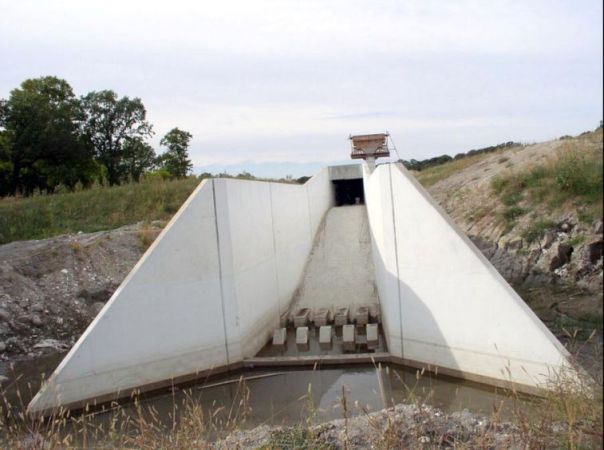
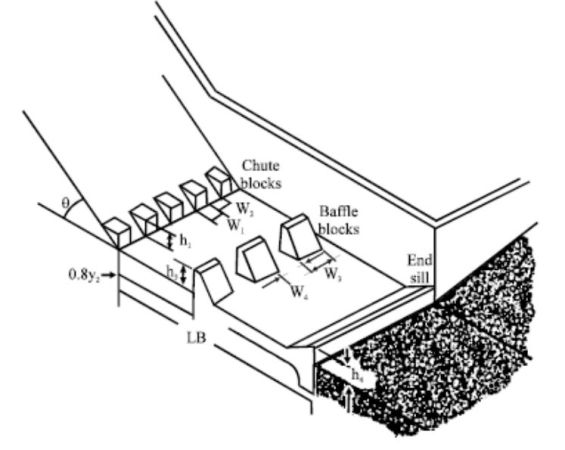
Type I Stilling Basin. Note: Chute Blocks, Baffle Blocks, End Sill.
-
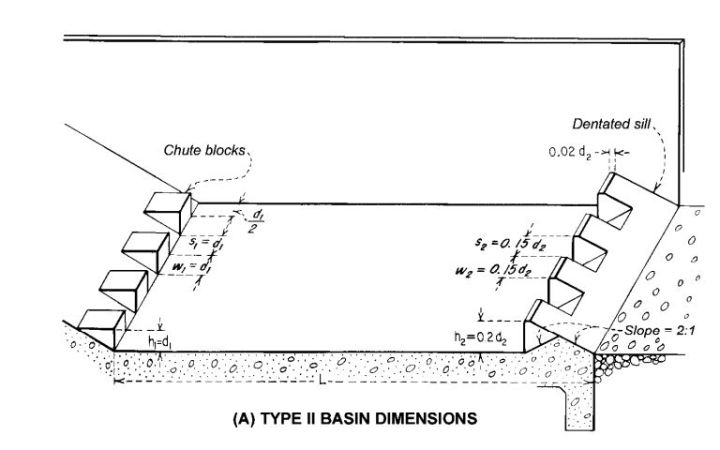
Type II Stilling Basin.
-
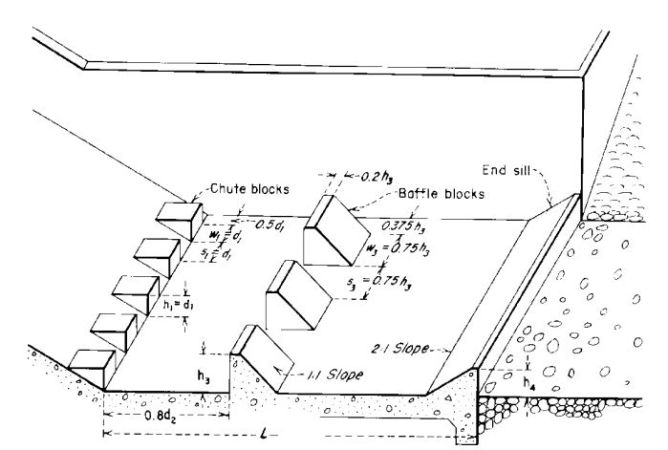
Type III Stilling Basin.
-
Type IV Stilling Basin.
-
A hydraulic jump in a 1:48-scale model of a Type V still basin for a spillway.
-
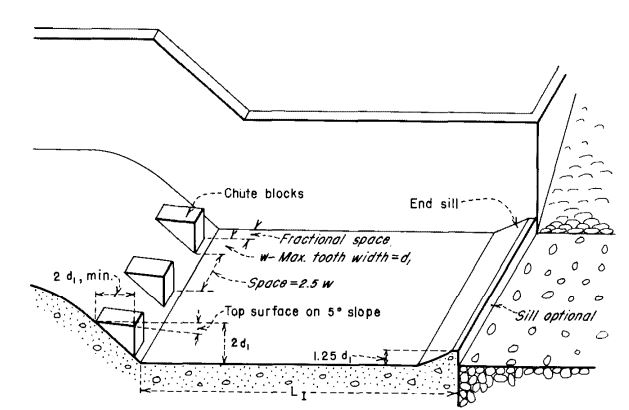
A photo taken from downstream of a SAF Stilling Basin.
Note: The content on this page was originally created as part of DamOutletWorks.org (DOWL, 2018). It has subsequently been updated and reformatted as part of the Dam Safety Toolbox.
Revision ID: 6784
Revision Date: 04/25/2023