Impact Basin Examples: Difference between revisions
From ASDSO Dam Safety Toolbox
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<!-- Add body paragraphs here --> | <!-- Add body paragraphs here --> | ||
Energy dissipation in an impact basin is accomplished through the turbulence created by the loss of momentum as flow entering the basin impacts a baffle, and the direction of the flow is changed. At high flow, further dissipation is produced as water builds up behind the baffle to form a highly turbulent backwater zone. | [[Energy Dissipation|Energy dissipation]] in an impact basin is accomplished through the turbulence created by the loss of momentum as flow entering the basin impacts a baffle, and the direction of the flow is changed. At high flow, further dissipation is produced as water builds up behind the baffle to form a highly turbulent backwater zone. | ||
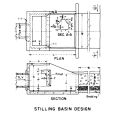
The type VI impact basin is a relatively small structure with highly efficient energy dissipation characteristics. This type of energy dissipation structure does not require tailwater control. | The type VI impact basin is a relatively small structure with highly efficient [[Energy Dissipation|energy dissipation]] characteristics. This type of energy dissipation structure does not require tailwater control. | ||
<gallery mode="slideshow" > | <gallery mode="slideshow" > | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
File:IB4.jpg|Layout for a Type VI Impact Basin | File:IB4.jpg|Layout for a Type VI Impact Basin | ||
File:IB5.jpg|Impact Basin with flow being discharged. | File:IB5.jpg|Impact Basin with flow being discharged. | ||
File:IB6.jpg|Type VI impact basins placed side by side. | File:IB6.jpg|Type VI [[Impact Basins|impact basins]] placed side by side. | ||
File:IB7.jpg|The end of this outlet conduit was constructed too close to the vertical hanging baffle resulting in intense sprayback. Lesson learned - follow design guidance! | File:IB7.jpg|The end of this outlet conduit was constructed too close to the vertical hanging baffle resulting in intense sprayback. Lesson learned - follow design guidance! | ||
File:IB8.jpg|Hook Basin | File:IB8.jpg|Hook Basin | ||
Latest revision as of 18:06, 27 April 2023
Energy dissipation in an impact basin is accomplished through the turbulence created by the loss of momentum as flow entering the basin impacts a baffle, and the direction of the flow is changed. At high flow, further dissipation is produced as water builds up behind the baffle to form a highly turbulent backwater zone.
The type VI impact basin is a relatively small structure with highly efficient energy dissipation characteristics. This type of energy dissipation structure does not require tailwater control.
Note: The content on this page was originally created as part of DamOutletWorks.org (DOWL, 2018). It has subsequently been updated and reformatted as part of the Dam Safety Toolbox.
Revision ID: 6792
Revision Date: 04/27/2023