Loads / Load Cases: Difference between revisions
Rmanwaring (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Delete any sections that are not necessary to your topic. Add pictures/sections as needed --> | <!-- Delete any sections that are not necessary to your topic. Add pictures/sections as needed --> | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
[[Category:Global Stability of a Dam]] | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
|link= | |link= | ||
<!-- Add picture caption --> | <!-- Add picture caption --> | ||
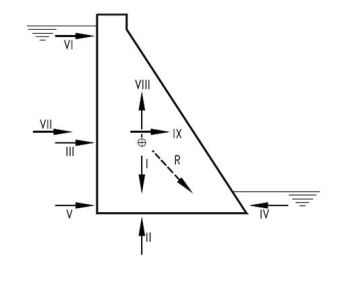
|caption= Free body diagram showing forces acting on a gravity dam. | |caption= Free body diagram showing forces acting on a gravity dam. | ||
(Image Source: [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Forces_Gravity_Dam.jpg Wikimedia]) | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
There are a variety of forces against which a dam should be designed to adequately resist including but not limited to: self-weight, static water pressures, wave pressures, sediment buildup pressures, uplift water pressures, wind pressures, thermal loads, ice pressures, and earthquake forces. | There are a variety of forces against which a dam should be designed to adequately resist including but not limited to: self-weight, static water pressures, wave pressures, sediment buildup pressures, uplift water pressures, wind pressures, thermal loads, ice pressures, and earthquake forces. | ||
"Design of civil works projects must be performed to ensure acceptable performance of all [[Reinforced Concrete|reinforced concrete]] hydraulic structures during and after each design event. Three levels of performance for [[stability]], strength, and stiffness are used to satisfy the [[structural]] and operational requirements for load categories with three expected ranges of recurrence (Usual, Unusual, and Extreme).<ref name="EM 1110-2-2104">[[Strength Design for Reinforced Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-2104) | Strength Design for Reinforced Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-2104), USACE, 2016]]</ref> | "Design of civil works projects must be performed to ensure acceptable performance of all [[Reinforced Concrete|reinforced concrete]] hydraulic structures during and after each design event. Three levels of performance for [[stability]], strength, and stiffness are used to satisfy the [[structural]] and operational requirements for load categories with three expected ranges of recurrence (Usual, Unusual, and Extreme).<ref name="EM 1110-2-2104">[[Strength Design for Reinforced Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-2104) | Strength Design for Reinforced Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-2104), USACE, 2016]]</ref> Minimum acceptable factors of safety for these load categories typically vary, with higher factors of safety required for usual conditions and lower factors of safety required for extreme conditions. | ||
==Best Practices Resources== | ==Best Practices Resources== | ||
{{Document Icon}} [[Earthquake Design and Evaluation of Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-6053) | Earthquake Design and Evaluation of Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-6053), USACE]] | |||
{{Document Icon}} [[Stability Analysis of Concrete Structures (EM 1110-2-2100) | Stability Analysis of Concrete Structures (EM 1110-2-2100), USACE]] | |||
{{Document Icon}} [[Earthquake Design and Evaluation of Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-6053) | Earthquake Design and Evaluation of Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-6053), USACE | {{Document Icon}} [[Ice Engineering (EM 1110-2-1612) | Ice Engineering (EM 1110-2-1612), USACE]] | ||
{{Document Icon}} [[Stability Analysis of Concrete Structures (EM 1110-2-2100) | Stability Analysis of Concrete Structures (EM 1110-2-2100), USACE | |||
{{Document Icon}} [[Ice Engineering (EM 1110-2-1612) | Ice Engineering (EM 1110-2-1612), USACE | |||
==Trainings== | ==Trainings== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:12, 21 July 2023
|
| Free body diagram showing forces acting on a gravity dam.
(Image Source: Wikimedia) |
There are a variety of forces against which a dam should be designed to adequately resist including but not limited to: self-weight, static water pressures, wave pressures, sediment buildup pressures, uplift water pressures, wind pressures, thermal loads, ice pressures, and earthquake forces.
"Design of civil works projects must be performed to ensure acceptable performance of all reinforced concrete hydraulic structures during and after each design event. Three levels of performance for stability, strength, and stiffness are used to satisfy the structural and operational requirements for load categories with three expected ranges of recurrence (Usual, Unusual, and Extreme).[1] Minimum acceptable factors of safety for these load categories typically vary, with higher factors of safety required for usual conditions and lower factors of safety required for extreme conditions.
Best Practices Resources
![]() Earthquake Design and Evaluation of Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-6053), USACE
Earthquake Design and Evaluation of Concrete Hydraulic Structures (EM 1110-2-6053), USACE
![]() Stability Analysis of Concrete Structures (EM 1110-2-2100), USACE
Stability Analysis of Concrete Structures (EM 1110-2-2100), USACE
![]() Ice Engineering (EM 1110-2-1612), USACE
Ice Engineering (EM 1110-2-1612), USACE
Trainings
![]() On-Demand Webinar: Introduction to Concrete Gravity Dams
On-Demand Webinar: Introduction to Concrete Gravity Dams
![]() On-Demand Webinar: Analysis of Concrete Arch Dams
On-Demand Webinar: Analysis of Concrete Arch Dams
![]() On-Demand Webinar: Stability Evaluations of Concrete Dams
On-Demand Webinar: Stability Evaluations of Concrete Dams
![]() On-Demand Webinar: Uplift and Drainage for Concrete Dams and Spillways
On-Demand Webinar: Uplift and Drainage for Concrete Dams and Spillways
![]() On-Demand Webinar: Seismic Stability Evaluation of Earth Dams
On-Demand Webinar: Seismic Stability Evaluation of Earth Dams
![]() On-Demand Webinar: Earthquake Hazards, Ground Motions and Dynamic Response
On-Demand Webinar: Earthquake Hazards, Ground Motions and Dynamic Response
![]() On-Demand Webinar: Delhi Dam – A Compound Failure
On-Demand Webinar: Delhi Dam – A Compound Failure
![]() On-Demand Webinar: Current Trends in the Seismic Analysis of Embankment Dams
On-Demand Webinar: Current Trends in the Seismic Analysis of Embankment Dams
Citations:
Revision ID: 7374
Revision Date: 07/21/2023
